SpotRM Web Help
SpotRM is an easy to use and intuitive web application.
Searches may be done either structure or text based. A structure search will highlight a potential reactive metabolite alert in the searched structure
while a text search will list drugs associated with your text string (more below).
To have an understanding of the basic concepts, we recommend reading of our perspective paper:
A. Claesson & A. Minidis, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018.
Also reading the Scope text helps to understand the selection and inclusion/exclusion of drugs and data.
In addition, these texts explain the advantages and limitations of using SMARTS (the underlying part of the search mechanism) as descriptions of RM alerts.
A list of the abbreviations used in the monographs and MiCs can be found here.
We strongly recommend that users set their web browser to open pdf files (i.e. monographs and MiCs) in the browser and not in a separate application; otherwise links in these files to other PDFs will not open.
Structure Search
Input:
Structures may be sketched with JSME, a free molecular editor by Bruno Bienfait and Peter Ertl
J. Cheminformatics 2013, 5:24.
Aside from drawing, you can paste structures as smiles, mol or sdf. If needed, visit their documentation at
JSME Help pages.
You can paste a SMILES or InChI string into the marked window. You can also upload files in the formats *.smi, *.sd, and *.sdf, which are automatically recognized. In a file with SMILES strings you can have a name attached, for example a SMILES file can have:
- Just SMILES, one per line,
- A SMILES followed by a compound name separated by a single whitespace character, in which case the compound name is used in the output. Note that white space characters are not allowed in compound names. An example line could be:
CCN(CC)CCNC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C1C)C=C2C3=C(C=CC(=C3)F)NC2=O)C Sunitinib
- A SMILES followed by a name followed by one or more data fields all separated by single whitespace characters. In this case the name is used and all subsequent fields dropped,
- An optional header line of any format.
If you do not have any SMILES directly available, here are a few that you can copy and test:
CCC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2O1)C(=O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3)Br)O)Br
CCCN(CCC1=CC=CS1)C2CCC3=C(C2)C=CC=C3O
CCN(CC)CCNC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C1C)C=C2C3=C(C=CC(=C3)F)NC2=O)C sunitinib
And here are a couple of InChI strings:
InChI=1S/C17H12Br2O3/c1-2-13-15(10-5-3-4-6-14(10)22-13)16(20)9-7-11(18)17(21)12(19)8-9/h3-8,21H,2H2,1H3
InChI=1S/C15H13ClFNO2/c1-9-5-6-13(10(7-9)8-14(19)20)18-15-11(16)3-2-4-12(15)17/h2-7,18H,8H2,1H3,(H,19,20)
Output
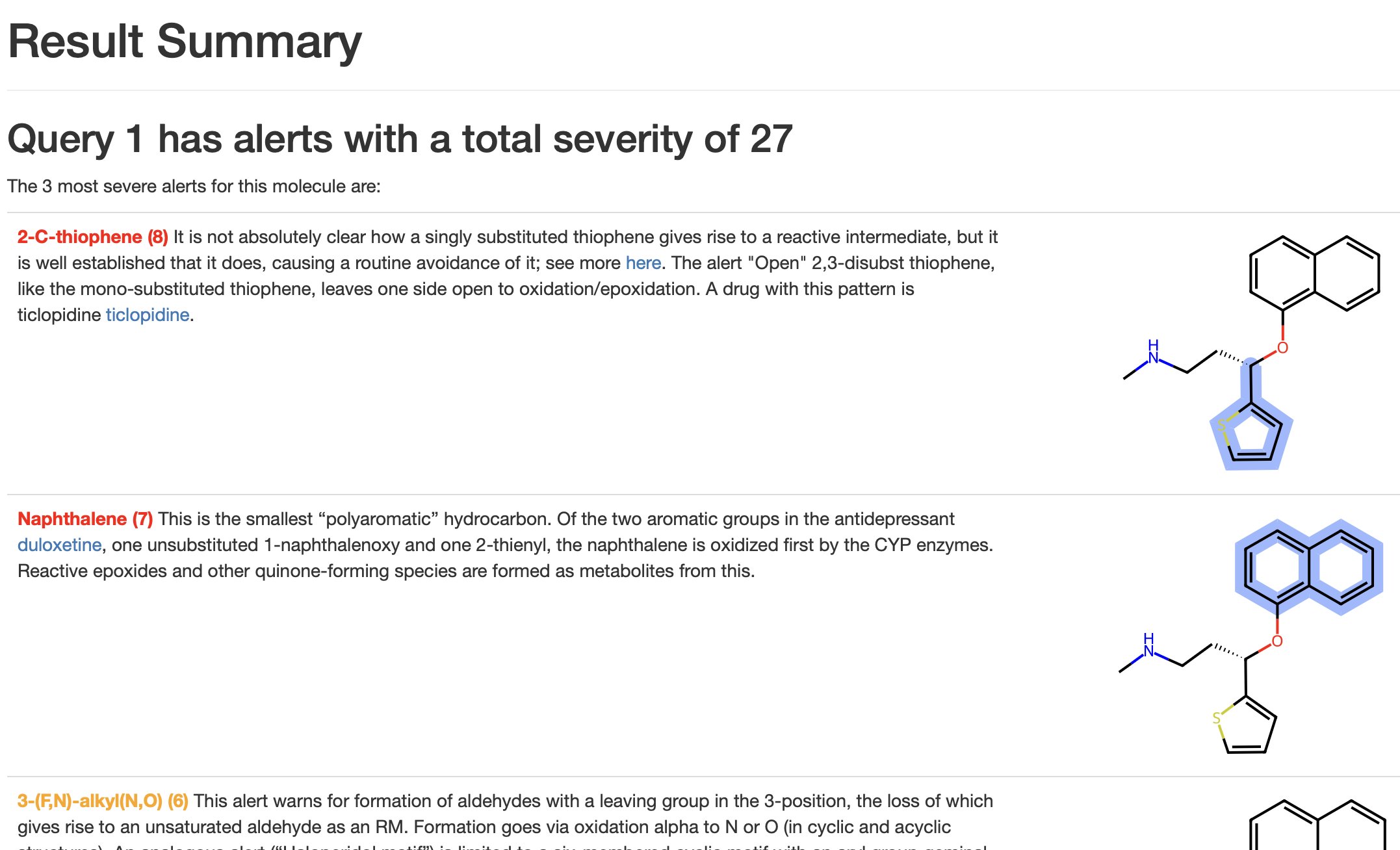
In our modern, 2025 released, result view, the top three severity hits with alert hits highlighted will be listed together with a 500 character (or less) summary of the alert, see picture below.
We hope this will render your analysis more efficient by reducing the number of potential drill-downs you might have to do.
The button on the bottom allows switching to the classical view ("Full Results"). You can also specify the classic view in advance using the toggle button on the search page.
Optionally, the classic view (Full Results) is still available with the input structures listed to the right in a table with alert hits highlighted (picture below).
Clicking a drug name gives its structure as a pop-up. Alerts for each input structure are listed in Severity order and a sum of these scores is listed in the header.
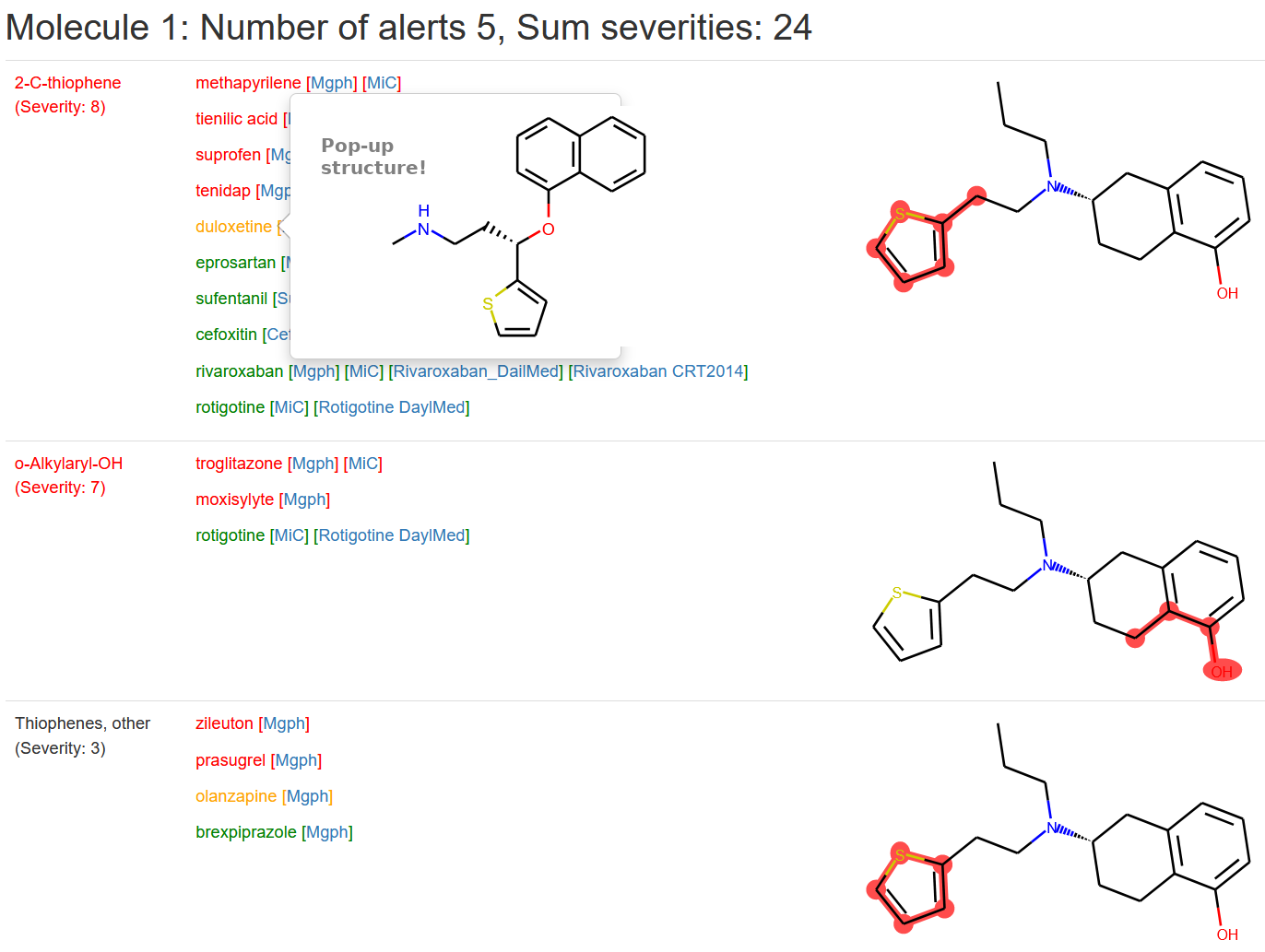 Severity score and Classification:
Severity score and Classification:
Severity is a number ranging from 1 to 10, with 1 being the least and 10 most severe structural alert mechanism(s). These numbers are not based on a mathematical formula,
but rather a combination of carefully curated multiple "soft factors".
For a more detailed explanation of the scoring system, see the
Scope text
and additionally the in depth
white paper on our Awametox website.
Text search
Text search covers:
- Drug names in the database. You can get a full listing of all 317+ drugs in the database by querying asterisk with an (⁎).
- Useful keywords listed in a PDF_text field: for example many pharmacological indications and mechanisms like antiepileptic, NSAID, antifungal, and analgesic etc. Important chemical groups, e.g. hydrazine, thiourea and lactam, can also be found there.
- Chemical names and known synonyms
- Market Status
Names of structural alerts are currently not searchable.
Output
Output is in a table based on drug names.
If you do not find an answer to your question you should send it to ✉ support and you are also welcome with suggestions for improvements.
REST API Searches
SpotRM also has a REST API which allows one to run searches from scripting environments such as python or Knime, or to integrate access to the SpotRM functionality into your inhouse systems. Several examples can be found here, including one showing how to retrieve a listing of all the available endpoints, and should show you enough of the API to get started with your own scripts or integration. Note that an active account is required to access the SpotRM API.
Further Reading
Acknowledgements
SpotRM Web depends on a number of open source components and libraries which are greatfully acknowledged and include:
- RDKit
- Open-source cheminformatics: http://www.rdkit.org (BSD-3 licence)
- Python Flask
- A lightweigh web application framework: https://palletsprojects.com/p/flask/ (BSD-3 licence)
- JSME
- B. Bienfait and P. Ertl, JSME: a free molecule editor in JavaScript, J. Cheminformatics 5:24 (2013) (BSD-3 licence)

